Module 1 - 19 pages: Background of GST And Constitutional Amendment
• In this course, we shall be covering the constitutional background of GST,
key definitions and concepts under GST, Levy, Time of Supply, Place of
Supply, Input tax credit, Valuation, Registration, Returns, Payments,
Refund, Assessment, Appellate proceedings, Offences and Penalties, etc.
• The objective of the course is to impart basic understanding of GST which
will be useful to professionals from finance or tax background for
compliance and record keeping required under GST.
In the current chapter, we will be covering the brief background behind introduction of GST and
constitutional background. The list of the key topic covered is summarized below :-
‒ What is Indirect Tax?
‒ Taxes subsumed under GST
‒ Why GST was introduced
‒ Benefits of GST
‒ Roadmap of GST Implementation
‒ Constitutional Background
‒ Procedure for Amendment in GST law
‒ Overview of GST legislation
‒ Rate Structure in GST Regime
‒ Key Stake Holders
‒ GST Council and its Role
‒ Exemption Carried forward from Earlier Tax regime
• Indirect taxes are the taxes levied on goods or services supplied by a person and collected from buyers.
• The tax is basically levied on the seller of the goods or the provider of the services
• The seller/ provider of services passes tax burden to the end consumer and therefore ultimately it is the end consumer who bears this in the form of Indirect Tax
• For instance, Goods and services tax means tax on supply of goods, or services or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption. GST on petrol, diesel and related products will be notified at later date.
Why GST?
- Cascading effect of taxation
- Multiple taxable events
- Double taxation of a transaction as both goods and Service
- Blocked credits
- Evolving laws Frequent changes
Roadmap:
GST – The Constitution of India has been amended by the Constitution (101st Amendment ) Act, 2016 for this purpose. Constitutional framework Article 246A - Union and States empowered to enact laws in relation to GST. The powers to make laws for inter-state supplies is exclusive to Union. Article 269A provides for making law in relation to inter-state supply of goods and services.
Article 269A provides for making law in relation to inter-state supply of goods and services.
Article 279A provides for constitution of GST Council.
174 Sections, rules, clarifications, circulars.
Present GST Tax Rate Structure is as follows**Additionally, compensation cess is levied for specified products.
Nil Rated:- Salt, Indian National Flag, duty credit scrips, etc.
5%:- Cream, Paneer, natural honey, etc.
12% :- Butter, candles, bicycles, contact lenses, etc.
18% :- Services like IT, telecom services, etc.
28% :- Pan Masala, Cigars, Cement, yachts, lottery, etc.
The process for creating GST Council started in India when the Constitution (One Hundred and Twentysecond Amendment) Bill 2016. GST Council was formed with Union Finance Minister as Chairperson, The
Union Minister or Ministers of State in-charge of Revenue or Finance for the following role:
Central or State Government grant exemptions in public interest which may be absolute or conditional
exemption. The illustrative list of exemption in earlier tax regime which were carried forward by the law maker in GST law as well are summarized below:
Type of Goods and Services Exempt under/Pre GST Regime/ Exempt under Post/ GST Regime
1. Agriculture products like fruits and vegetables, etc. Yes Yes
2. Services by way of admission to a museum, national park, wildlife
sanctuary, tiger reserve or zoo Yes Yes
3. Service provided by arbitral tribunal to specified entities Yes Yes
4. Services by a veterinary clinic in relation to health care of animals
or birds Yes Yes
5. Funeral Services Yes Yes
Module 2: Important Definitions. 11 Pages.
1. Understand some definitions:

- 2(52) Goods cover all (1) movable property (2) but not money and securities (3) include actionable claims like crops attached to land not severed (GST will be applicable - you might have exemption)
- 2(102) Services (1) anything other than goods (2) exchange of money (3) facilitating or arranging transaction in securities.
- 2(31) Consideration - (1) Payment made or to be made by money or otherwise even grants (2) Advance deposit only if there is a consideration
- 2(17) Business (1) any trade, commerce, manufacture (2) provision by club, association, society (3) admission to premises
- Composite supply - Bundled. One principle umbrella and multiple others.
- Mixed supply 2(74) - Single price - different products with different GST rate - whatever the highest rate that would be applicable on other supplies. Example: Mobile with charger, earphone and other accessories (BOGIF - Buy one get one free will not fall in either 5 or 6)
- Continuous supply of Goods and another for Continuous supply of Services.
- Taxable and Non Taxable supply 2(18) and 2(78) Not covered example petroleum, liquor, Schedule 3.
- Works contract - Immovable property
- Recipient 2(39) - making payment, if not taking delivery or service
- Supplier 2(105) - supplying goods/services or agent
- Exempt Supplier 2(47) - Supply of any goods or services or both which attracts nil rate of tax, Wholly exempt from tax under section 11, or under section 6 of the IGST Act, Includes non-taxable supply
- Reverse Charge Section 2{98}: Liability of tax payable by recipient of notified goods or services
- Aggregate Turnover Section 2{6}: Very important definition - as based on it it would depend if you need to take registration?
- Aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding reverse charge)
- Exempt supplies
- Exports of goods/ services
- Inter-state supplies for same PAN
- Tax Period Section 2{106}: Period for which the return is required to be furnished; Monthly, quarterly, annual returns are to be files.
Module 3: Concept of supply under GST. 7 Pages.
Pre GST event: Exercise - taxable event was manufacture; VAT - Sale; Service - Event
All these events combined and is called Supply.
8 limbs and 2 provisio.
- Sale - ownership change
- Transfer - no change in ownership; goods moving from one branch to other
- Barter
- Exchange
- License
- Rental
- Lease
- Disposal - Depreciated assets
For consideration, in the course of business.
Proviso:
- Import of service
- Schedule 1 items - supply without consideration.
Supply is an inclusive definition.
Supply - Schedule 1
Supply - Schedule 11
Goods:
Activities to be treated as supply of goods
- Transfer of title in goods
- Transfer of title where property will pass at future date
- Goods cease to form part of business assets
- Transfer of assets where person ceases to be a taxable person
- (except where as a going concern or by a personal representative)
- Supply of goods by unincorporated association to its member
Supply of Services:
Supply- Schedule III: Supply of neither goods nor services
Sec. 7(2)(b) Such activities or transactions undertaken by
• Central government
• State government
• Any local authority
where they are engaged as public authorities. (as may be notified)
Module 4: Registration under GST 14 pages
Registration is the prerequisite for doing a business, but not all need to. Section 22 to Section 30 discuss registration.
If business in 15 states - need registration in all the states
Turnover:
Supplier of Goods
- Aggregate turnover > 40 lakhs (intra state turnover)
- Aggregate turnover >10 lakhs (intra state turnover for suppliers located in special category states*)
Supplier of services
- Aggregate turnover > 20 lakhs (inter or intra state turnover)
- Aggregate turnover >10 lakhs (turnover for suppliers located in special category states*)
Not liable for registration
1. Exclusive exempt supplier of goods or service
2. Where recipient is liable to pay tax under RCM
3. Certain taxpayers who are making supplies through e-commerce operator.
“Aggregate Turnover" means aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding value of inward supplies on which tax is
payable on reverse charge mechanism, exempt supplies, export of goods or services or both Inter-state supplies of
persons having the same PAN (to be computed on all India basis) but excludes central tax, state tax, union territory tax,
integrated tax and cess and includes all supplies made by the taxable person, whether on own account or made on behalf of all his principals
Voluntary registration
A person who is not liable for registration may still choose to obtain voluntary registration, all provisions of the Act as are applicable to a registered person, shall apply to such voluntary registered person. Benefits of Voluntary registration:
- Availing and passing on Input tax credit
- Good Rating under GST may help in increasing the scale of operations and adding more customers
- Renting premises, availing loans from banks and other such business requirements will become easier for businesses that are registered
Compulsory registration
Point 8 certain people might get exemption.
Time limit and Process of Registration
Time limit for registration
• Within 30 days from the date on which the person becomes liable
• A casual taxable person or a non-resident taxable person shall apply for registration at least 5 days prior to the commencement of business
Process of registration
• Application of registration filed by the taxable person along with Aadhar authentication
• Proper officer on receipt of application shall examine the details and if details are found in order, approve the same within seven working days
• If the application submitted is found to be deficient, communication must be made in Form REG-03 within 7 working days from date of submission of application
• Reply to the said notice shall be made in Form REG-04 within a period of 7 days from date of receipt of notice
• Where application is not approved by the officer within the due time limit, application for registration shall be deemed to have been approved.
Composition Scheme
- Composition dealer is not allowed to collect outward tax from customers
- Not allowed to avail Input tax credit
- Required to pay tax through GST CMP-08 quarterly and furnish GSTR-4 and GSTR-9A annually
- Required to issue Bill of Supply instead of Tax Invoice
Composition scheme – Sec. 10
10(1) r/w 10(2)
Composition scheme - I
• Aggregate Turnover in preceding financial year ≤150lacs (75 lacs for specified states)
• Services along with goods can be supplied up to 10% of turnover in state (preceding financial year) or 5 lakh rupees, whichever is higher.
• Tax rate – Refer Annexure A
• Liable to pay tax under
reverse charge u/s 9(3) and
9(4) at applicable rates
10(2A)
Composition scheme - II
• Applicable for suppliers not eligible to pay tax under 10(1) r/w 10(2)
• Aggregate Turnover (preceding financial year) not exceeding 50 lacs
• Tax rate – 6% for suppliers opting or said scheme
• Liable to pay tax under reverse charge u/s 9(3) and 9(4) at applicable rates
Eligibility
• Not engaged in making any supply of goods or services which are not leviable to GST
• Not engaged in making any interState outward supplies
• Not engaged in making any supply through an electronic commerce operator required to comply with sec 52
• Not a manufacturer as may be notified by the Government
• Neither a casual taxable person nor a non-resident taxable person
10(1) r/w 10(2)
Composition scheme - I
• Aggregate Turnover in preceding financial year ≤150 lacs (75 lacs for specified states)
• Services along with goods can be supplied up to 10% of turnover in state (preceding financial year) or 5 lakh rupees, whichever is higher.
• Tax rate – Refer Annexure A
• Liable to pay tax under reverse charge u/s 9(3) and 9(4) at applicable rates
10(2A)
Composition scheme - II
• Applicable for suppliers not eligible to pay tax under 10(1) r/w 10(2)
• Aggregate Turnover (preceding financial year) not exceeding 50 lacs
• Tax rate – 6% for suppliers opting for said scheme
• Liable to pay tax under reverse charge u/s 9(3) and 9(4) at applicable rates
Eligibility
• Not engaged in making any supply of goods or services which are not leviable to GST
• Not engaged in making any interState outward supplies
• Not engaged in making any supply of services through an electronic commerce operator required to comply with sec 52
• Not a manufacturer as may be notified by the Government
• Neither a casual taxable person nor a non-resident taxable person

Documents needed:
Cancellation of registration
Revocation of cancellation of registration
• Application for revocation: Any registered person whose registration is cancelled by the
proper officer on his own motion, may apply to such officer for revocation of cancellation of
registration in such manner, within such time and subject to such conditions and
restrictions, as may be prescribed.
• Acceptance or Rejection of application by proper officer: The proper officer may in
such manner and such period as may prescribed, by order, either revoke cancellation of
registration or reject the application
Provided that application for revocation of cancellation of registration shall not be rejected
unless the applicant has been given an opportunity of being heard.
Module 5 PPT 35 Concept of Place of Supply under GST.
Place and location determine nature of supply i.e. interstate or intra state.
Any interstate supply IGST will be applicable and intra state it will be, CGST or SGST or UTGST depeding on the location.
Relevance of Place of Supply (POS)
• POS has been defined under IGST Act
• POS along with location of supplier determines nature of supply i.e. whether supply is inter-state or intra state
Location of recipient and supplier has been defined under GST basis place of business .
• Specific cases have been provided in law wherein levy of GST has been pre-determined. In case of supply from DTA to SEZ, IGST would be levied and same is always treated as an inter-state transaction. Similarly, imports of goods and services are inter-state supplies.
Place of Supply (POS) of goods in other miscellaneous cases:
“export of goods” with its grammatical variations and cognate expressions, means taking goods out of India to a place outside India [Section 2(5) of the IGST Act,2017]
Nature of Transaction Place of Supply
Goods supplied on board a conveyance [Sec. 10(1)(e)] Location where goods are taken on board
Import into India [Sec. 11(1)] Location of importer
Export from India [Sec. 11(2)] Location outside India
Place of Supply (POS) of goods: Bill to – Ship to (Out of India)
Nature of Transaction Understanding Place of Supply
Bill to in India –Ship to out of India
[Sec. 10(1)(b)]
• Direction given by Indian (Bill to) party
• Movement of goods outside India results transaction
into Export for the bill to party
• Principal place of business of person
giving the direction
Bill to out of India – Ship to in
India
[Sec. 10(1)(b)]
• Movement is within India, thus not export of goods
• Shipped to location not relevant for determining
place of supply
• Location outside India since the
person giving the instruction is
outside India. In such a case IGST
would be charged
Place of Supply of Services
Place of Supply (POS) of services where both supplier and recipient are located in India
POS of services shall be guided by general rule [Sec. 12(1)] as mentioned below (except in case of specific services):
Transaction: Supply of restaurant and catering services, personal grooming, fitness, beauty treatment, health service including cosmetic and plastic surgery [Sec. 12(4)]
Place of supply: Location where services are actually performed
(Not all data included)
Module 6: Time and Value of Supply PPT: 12
Time is relevant, because Tax is applicable from the time of supply on the value of supply.
Module 7: Input Tax Credit: PPT 12
Very important topic = Cash.
It can be utilised against output tax credit.
Input Tax under GST
Definition Sec. 2(62) - • CGST/ SGST/ IGST/ UTGST charged on supply of goods or
services
Inclusion Sec. 2(62)
• IGST on imports
• CGST/ IGST/ SGST/ UTGST paid under reverse-charge
Exclusion • Tax paid under composition levy
Time-limit Sec. 16(4): • Earliest of filing return for September* following end of the financial year or annual return
**Under finance bill 2022, an amendment has been proposed to substitute ‘due date of filing return for September’ with ’30 November’
following end of the FY. This amendment will be applicable from such date as may be appointed by a notification
First and formost condition is that the invoice has to be raised.

Other Conditions:
- Invoice, debit note, self invoice, ISD invoice/credit note and bill of entry or other document prescribed in Custom Act,1962 can be used.
- Receiver of ITC can avail credit in respect of invoices and debit notes which have been furnished by supplier in GSTR-1/ IFF and appearing in GSTR-2B
- Banking company have an option to comply with sec. 17(2) i.e. either to reverse the credit pertains to exempt supply for example interest received or may claim 50% of ITC eligible.
- Rule 41 of CGST Rules, 2017 have also provided provision for transfer of credit in case of sale, merger, de-merger, amalgamation, lease or transfer of business.
ITC – Goods sent for Job work
Job worker is not the principal, he is just doing on behalf of principle.
Note: - Above conditions does not applies to moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures, or tools sent out to a job worker for job work.
Input: has to be return within one year. Maintain books of accounts.
Capital Goods: Return period of capital goods is 3 years.
This is not applicable for liquor and petroleum and its products as they are covered separately by state.
Formula to be applied on a monthly and yearly basis,
keep knocking of the credit in this order.
Mechanism to utilise to knock of the credits.
Thumb rule - IGST must be fully utilised before utilising the other.
Module 8: Input Service Distributor: PPT 8
Input Service Distributor means an office of a supplier which receives tax invoices towards the receipt of input services and distributes credit of GST paid to its branch offices.
Points for Consideration:
Invoice should contain:
- Name, address, GSTIN of ISD and recepient
- A consecutive serial number
- Date of issue
- Amount of credit distributed
- Signature authorised representative
ISD shall only deal with input services. It cannot keep credits in its own books.
Module 9: Job Work and TDS/TCS - Page 10
Job work is supply of service.
• Ownership of goods belongs to Principal andtreatment or process on such goods are undertaken by job worker.
• As per Schedule II of CGST Act, “Any treatment or process which is applied to another person's goods is a supply of services.” Hence, Job work is a supply of Service.
• The principal is allowed to avail credit on the goods directly sent to the job worker.
Job work - Procedure:
Inputs or capital goods can be sent by a principal to job worker without payment of tax under a Delivery Challan along with e-way bill, if applicable.
• Inputs or capital goods can be supplied from business premises of unregistered job worker if principal has added it as additional place of business.

Job Work – Other Provisions
• Principal may on intimation, send and bring back goods from “Job Worker” to any of his place of business without payment of tax provided the goods are returned within the prescribed time limit as summarized below:
• Type me Limit
- Inputs (whether completed or otherwise) - 1 year
- Capital Goods (other than moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures, or tools) - 3 Year
• If Inputs or Capital Goods (other than other than moulds and dies, jigs and fixtures, or tools) are not returned
within prescribed time limit, it shall be considered as deemed supply on the date when such goods were
received by the job worker.
• Waste and scrap generated during job work may be supplied on payment of tax by job worker, if job worker is
registered or by principal, if job worker is unregistered.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
Person required to deduct TDS
• Department / Establishment of Central Government /State Government
• Local Authority
• Government Agencies
• Other person notified by the government
Transaction Value • Where total value of such supply of goods and / or services under acontract exceeds INR 2.5 lakhs.
• Taxable value of supply excluding GST indicated in invoice needs to be
considered for deduction.
Rate • 1% CGST + 1% SGST [2% in case of IGST] of payment made or credited
to the supplier
Non-Applicability of TDS
• If location of supplier and place of supply is in a state different from the
state of registration of the recipient
Time Limit of Payment • 10th day of the succeeding month in which deduction has been made
Interest for delayed
payment
• Interest at the rate notified, not exceeding 18% to be paid
Certificate • Certificate in Form GSTR-7A will be made available in GST portal once
return is filed
Excess / Erroneous Deposit
• Refund shall be according to Section 54
• No refund to deductor if the amount has been credited to electronic cash ledger of the deductee
Claim in Electronic Cash Ledger by Deductee
• Deductee shall claim the credit in his electronic cash ledger of the amount of deduction made by the deductor
Tax Collected at Source (TCS)
Person required to
collect TCS
• E-commerce operator (not agent) shall collect TCS on taxable supplies made
through it by other supplier, where consideration with respect to such
supplies is to be collected by the operator
Rate • 0.5% CGST + 0.5% SGST [1% IGST] of net value of taxable supplies made
through it
Net Value of Taxable
Supplies
• Aggregate value of taxable supplies of goods and/or services made through
e-commerce operator excluding supplies notified under Section 9(5) of CGST
Act and value of taxable supplies returned
Time Limit of Payment • 10th day of the succeeding month in which collection has been made
Interest for delayed
payment
• Interest at the rate notified, not exceeding 18% to be paid
Furnishing of Statement • Monthly- on or before 10th of succeeding month in Form GSTR-8
• Annually- on or before 31st December following the end of the financial year
• Rectification- before due date of filing of return for the month of September
following the end of the financial year or actual date for furnishing of the
relevant annual statement, whichever is earlier
Claim in Electronic
Cash Ledger
• Collectee shall claim the credit in his electronic cash ledger of the amount
of tax collected by the collector
Module 10: Payment of Tax under the GST Law PPT 15 pages.
Introduction
Format of Liability Register, Electronic Credit Ledger and Electronic Cash Register
• Payment of tax is to be made on or before 20th of succeeding month.
• A unique identification number shall be generated for every debit/credit made in electronic liability register, electronic credit
register and electronic cash register.
• Every taxable person shall discharge his tax and other dues under this Act in the following order:
o Self-assessed tax and other dues related to previous tax periods
o Self-assessed tax and other dues related to current tax period
o Any other amount/demand payable under section 73 or section 74
• Mode of Payments are summarized below:
- Internet banking
- Credit Card or Debit card
- NEFT/RTGS
- Over the counter (OTC)
- OIDAR Services - international money transfer through Society for Worldwide Internet banking

Electronic Liability Register
Applicability • This register is applicable for every person liable to pay tax, interest, penalty, late fee or any other amount
Form • GST PMT-01
Items to be Debited
• Amount of tax, interest, late fees or any other amount payable as per return
• Amount of tax, interest or any other amount payable as determined by proper officer
• Amount of tax & interest payable due to mismatch under section 42 & section 43
• Amount of interest that may accrue from time to time
Payment made to be credited • Every payment has to be made either from electronic cash ledger or electronic credit ledger
Miscellaneous
• Amount of demand debited shall stand reduced to the extent relief given by proper officer or appellate tribunal or court by way of credit in register
• Amount of penalty imposed or liable to be imposed shall stand reduced to the extent of payment made of tax interest or penalty by way of credit in register
Discrepancy
• If the registered person notices any discrepancy in the register, communicate the same to the officer exercising jurisdiction in
Form GST PMT-04

Electronic Credit Register
Applicability • This register is applicable for every registered person eligible to take ITC
Form • GST PMT-02
Items to be Debited
• Amount of liability discharge through input tax credit
• Amount of refund claimed, if any
Items will be Credited • Eligible input tax credit
Miscellaneous • If the amount of refund claimed is rejected, amount debited earlier shall be re-credited to electronic credit ledger
Discrepancy
• If the registered person notices any discrepancy in the register, communicate the same to the officer exercising jurisdiction in
Form GST PMT-04
These registers are auto populated and no manual intervention is allowed.

Electronic Cash Register
Applicability • This register is applicable for every person liable to pay tax, interest, penalty, late fee or any other amount
Form • GST PMT-05
Items to be Debited • Amount of liability discharged through this register
Items to be Credited • Deposit made through Internet banking, credit/debit card,
NEFT, RTGS & OTC
Miscellaneous
• Any payment made in this register shall be made after generating challan in Form GST PMT-06 and his challan will be valid for 15 days.
• Where payment is made by way of NEFT/RTGS, mandate form will be generated and that mandate form shall be submitted to the bank from where payment is made and this mandate form shall be valid for 15 days.
• On successful credit of the amount to the account of the Govt., CIN will be generated by collecting bank
• On receipt of CIN, amount deposited shall be reflected in the electronic cash ledger of the concerned person
• In case any refund is claimed from this register, refund amount shall be debited in this register. If the refund claim made is rejected by proper officer, amount to the extent of rejection shall be credited to this register
Discrepancy
• If the payment amount is debited but no CIN has been generated, registered person shall communicate in Form GST PMT – 07 through the common portal to the bank or electronic gateway through which deposit was initiated
• If the registered person notices any discrepancy in the register, registered person shall communicate the same to the officer exercising jurisdiction in Form GST PMT-04
Format of Challan
Format of GST PMT-09
With effect from 1st January 2020, CBIC has inserted section 49(10), as per which Tax Payers are eligible to transfer the fund available in cash ledger balance of any Tax Head such as CGST, SGST & IGST to other Head such as SGST or IGST, CGST or IGST and CGST or SGST via filing of GST PMT-09.
Module 11: Documents prescribed under the GST law 18 pages.
Tax Invoice
Section 31 of CGST Act
• Supply by a registered taxable person under GST is to be made under a cover of “Tax invoice”
• “Tax invoice” is to be issued before or at the time of removal of goods in case of supply of goods
whereas it can be issued within 30 days of completion of services in case of supply of services
• For supply of goods, “Tax invoice” is to be issued in triplicate
• For supply services, “Tax invoice” is to be issued in duplicate
In case of continuous supply of goods, where successive statements of accounts or successive payments are involved, the invoice shall be issued before or at the time each such statement is issued or, as the case may be, each such payment is received.
In case of continuous supply of services, where the due date of payment is ascertainable, the invoice shall be issued on or before the due date of payment otherwise receipt of payment. In case, payment is linked to the completion of an event, the invoice shall be issued on or before the date of completion of that event.
E-invoicing - Overview
To automatically create invoice and curb tax evasion.
Bill of Supply
• A registered person supplying exempted goods/services or
• Paying tax under composition scheme
Payment voucher, Receipt voucher, Refund voucher
Payment voucher : A registered person liable to pay tax in cases of supplies from unregistered vendor/ supplies that attract tax liability on RCM basis and At the time of making payment to supplier
Reciept voucher : A registered person receiving advance payment with respect to any supply of goods/services
Refund voucher : A registered person received payment in advance, but no subsequent supply made, and no tax invoice issued.
Credit Notes and Debit Notes/Supplementary Invoices - Section 34 of CGST act.
ISD Invoices: • An input service distributor issues ISD invoices to distribute the GST ITC that pertains to different GSTIN having the same
PAN
Delivery Challan: Supply of liquid gas where the quantity at the time of removal is
not known
• Transportation of goods for job work
• Transportation of goods for reasons other than by way of supply
Tax Invoice in special cases are:
Supplier/Supply Document Requirement
Insurer or a banking company or a financial institution, including a non-banking
financial company
Consolidated tax invoice for supply made during themonth /any other document in lieu thereof
• Serial no. is not mandatory
• Address of the recipient not mandatory
• Signature of supplier is not mandatory
• Can be issued physically or electronically
• Other information as mentioned under rule 46 is required
Goods transport agency (GTA) Tax invoice or any other document in lieu thereof
• Gross weight of the consignment
• Name of the consigner and the consignee
• Registration number of goods carriage
• Details of goods transported
• Details of place of origin and destination
• GSTIN of the person liable for paying tax whether as consigner, consignee or goods transport agency, and
• Other information as mentioned under rule 46.
Passenger transportation service
Tax invoice • Ticket in any form, by whatever name called
• Serially number is not mandatory
• Address of the recipient of service is not mandatory
• Signature of supplier is not mandatory
• Containing other information as mentioned under rule 46.
Admission to exhibition of cinematograph films in multiplex screens
An electronic ticket • Details of the recipient of service is not mandatory
• Other information as mentioned under rule 46.
Module 12: Accounts and Records Page 7
Manner, period and place to be maintained.
Accounts and records to be maintained by every registered person
• production or manufacture of goods;
• inward and outward supply of goods or services or both;
• stock of goods;
• input tax credit availed/claimed;
• output tax payable and paid;
• goods or services imported or exported
• payment of tax on reverse charge along with the relevant documents
• advances received, paid and adjustments made thereto
• names and complete addresses of suppliers/recipients and
• such other particulars as may be prescribed
Records prescribed for Specified Cases
Supplier other than composition tax payer
• Accounts of stock in respect of goods received and supplied by him, and such accounts shall contain particulars of
opening balance , receipt, supply, goods lost, stolen, destroyed and balance of stock
• Account of tax payable, paid , input tax credit claimed
Agent
• Particulars of authorization received from principal for supply of goods on behalf of such principal
• Particulars including description, value and quantity of goods or services supplied and received on behalf of principal
• Details of accounts furnished to every principal and tax paid on receipts or supply.
Manufacturer Monthly production accounts showing quantitative details of raw materials or services used in the manufacture and quantitative
details of goods so manufactured including waste thereof.
Service provider Maintain accounts showing quantitative details of goods used in the provision of services, details of input service utilized and
services supplied.
Person executing works contract
• The names and addresses of the persons on whose behalf the works contract is executed.
• Description, value and quantity of goods or services received and utilized for execution.
• Details of payment received
• The names and addresses of the suppliers from whom he received goods or services.


Module 13 E-Way Bill PPT: 10
01 What is the E-Way Bill?
01 What is an Electronic Way Bill?
• An electronic document that is required for movement of goods.
• It has to be generated on e-way bill portal
• A movement of goods for more than INR 50,000/- in value cannot be made by a registered person without an e-way bill
02 When E-way bill has to be generated?
When there is movement of goods:
• In relation to supply
• For reasons other than a supply
• Due to inward supply from an unregistered person
03 Objective and benefits of E-Way Bills
04 Who can generate an E-Way Bill
05 Exceptions of generation of E-Way Bill
06 Consequences of not carrying E-Way Bill
07 Validity and Cancellation of E-Way Bill
Module 14: Refund of GST: Page 25
Refunds under GST
Refund – Explanation 1 to sec. 54 – Inclusive definition
➢ Refund of tax paid on zero-rated supplies of goods or services or both
➢ Refund of inputs or input services used in making such zero-rated supplies
➢ Refund of tax on the supply of goods regarded as deemed exports
➢ Refund of unutilized input tax credit due to a higher tax rate on the input than tax rate on outward supplies
Relevant provisions regarding Refunds
➢ CGSTAct – Sec. 54 to 58
➢ CGST Rules – Rule 89 to 97A

Cases where no refund shall be allowed
Cases where refund of unutilized ITC shall not be allowed
•In the cases other than:
oZero rated supply without payment of tax;
oAccumulation of ITC on account of inverted duty structure;
• Goods subject to export duty;
• If the supplier has availed drawback in respect of central tax or claims refund of the integrated tax paid on such supplies
Unjust Enrichment
• Every person who has paid tax to Govt. is assumed to have passed on the burden of tax, unless contrary is proved;
• As per principal of unjust enrichment, refund shall be given to person who has actually borne the burden of tax;
• Otherwise, refund is transferred to consumer welfare fund.
Non Payment of refund:
• No refund shall be paid if the amount of refund is less than ₹1,000 in each tax head separately.
Other relevant forms:
RFD-01W The applicant can withdraw the refund application during anytime before order of sanctioning of refund using RFD-01W
PMT-03 Where any amount claimed as refund is rejected, either fully or partly, the amount debited, to the extent of rejection, shall be re-credited to the electronic credit ledger under FORM PMT-03
Procedure for filing refund application on the portal
1. Under ‘Refunds’ select the tab ‘Application for refund’, select the category of refund from the following which you require to file.
2. Select the period for which you require to file refund application and click on create application. Select the refund type
3. Download the offline tool from the ‘Download offline utility’ option as available
4. Proceed to fill in details in relation to outward supplies for which refund is to be filed. Once all the details have been filled, proceed to create file to upload the same on the link mentioned in the previous slide.
5. Proceed to upload the file generated in the previous slide to the ‘Click to upload the details of exports of goods and/ or services’ section mentioned in the below image and validate the same.
6. Proceed to fill the turnover as computed and input tax credit availed for the relevant period. Maximum amount of refund eligible will get auto-populated.
7. Amount of refund claimed should be in compliance with the latest circulars issued by government. Further, amount eligible should be punched in the‘Refund to be claimed’ tab
8. Select the bank account in which you want the refund to be received.
9. Upload the documents in supporting of the refund claim to be made.
10. Click on the mandatory undertakings and proceed to provide LUT number (in case of exports without payment of tax) and proceed to save the return.
11. Review the entire application and proceed to submit the application.
12. Post submission, affix DSC to the application, Application will be re-directed to the concerned officer for processing.

Checklist – Refund of tax paid on export of services
S.no Refund Document Checklist
1 Declaration under second and third proviso to section 54(3)
2 Undertaking in relation to sections 16(2)(c) and section 42(2)
3 Statement 2 under rule 89(2)(c)
4 BRC/FIRC /any other document indicating the receipt of sale proceeds of services
5 Copy of GSTR-2A of the relevant period
6 Statement of invoices (Annexure-B)
7Self-certified copies of invoices entered in Annexure-A whose details are not found in GSTR2A of the relevant period
8Self-declaration regarding non-prosecution under sub-rule (1) of rule 91 of the CGST Rules
for availing provisional refund
Checklist – Accumulated ITC Refund
S.no Refund Document Checklist
1 Declaration under second and third proviso to section 54(3)
2 Undertaking in relation to sections 16(2)(c) and section 42(2)
3 Statement 3 under rule 89(2)(b) and rule 89(2)(c)
4 Statement 3A under rule 89(4)
5 Copy of GSTR-2A of the relevant period
6 Statement of invoices (Annexure-B)
7 BRC/FIRC in case of export of services and shipping bill (only in case of exports made
through non-EDI ports) in case of goods
Checklist – Inverted Tax Structure
S.no Refund Document Checklist
1 Declaration under second and third proviso to section 54(3)
2 Declaration under section 54(3)(ii)
3 Undertaking in relation to sections 16(2)(c) and section 42(2)
4 Statement 1 under rule 89(5)
5 Statement 1A under rule 89(2)(h)
6Self-declaration under rule 89(2)(l) if amount claimed does not exceed two lakh rupees, certification under rule 89(2)(m) otherwise
7 Copy of GSTR-2A of the relevant period
8 Statement of invoices (Annexure-B)
Module 15: Returns: Page 62
01 Returns under GST
02 Types of returns
IFF - Invoice Furnishing Facility - small tax payers - can give invoice details on a monthly basis
03 Filing of GSTR-1
04 Filing of GSTR-3B
05 GSTR-09
06 GSTR-09C
GSTR-9: Annual Return
GSTR 9 is an annual return to be filed once in a year by the registered taxpayers under GST including
those registered under composition levy scheme but excluding Casual Taxable person, Input Service
Distributors, Non-resident taxable persons and person paying TDS under section 51 of CGST Act.
GSTR-9 consists of details regarding the supplies made and received during the year under CGST,SGST
and IGST. It consolidates the information furnished in the monthly/
quarterly returns filed during the year
GSTR-9 shall be filed on or before 31st December of the subsequent
financial year.
For instance for FY 2020-21, the due date for filing GSTR 9 is
31st December 2021
A registered person shall not be allowed to furnish an annual return for a financial year after the expiry of
a period of three years from the due date of furnishing the said annual return- Inserted vide THE
FINANCE ACT, 2023 dated 31-03-2023 w.e.f. 01-10-2023
GSTR-9 – Details to be Provided
PART I Basic details of the taxpayer. This will be auto-populated.
PART II Details of outward and inward supplies declared during the financial year.
PART III Details of ITC for the financial year
PART IV Details of tax paid as declared in returns filed during the F.Y.
PART VI Other Information comprising of GST Demands and Refunds, HSN wise summary and
Late fee payable and paid details
GSTR-9C: Reconciliation statement
GSTR 9C is a statement of reconciliation between GSTR-9 filed and the amount as per the audited
financial statement of the taxpayers. As per Sec. 44 read with Rule 80, every registered person (whose
whose aggregate turnover during a financial year exceeds five crore rupees), other than Input Service
Distributor, a person paying tax under Sec. 51 or 52, a casual taxable person and a non-resident taxable
need to furnish this statement on self certification basis.
GSTR-9C shall be filed on or before 31st December of the subsequent
financial year.
For instance, FY 2020-21 due date for filing GSTR 9C is
31st December 2021
GSTR-9C – Details to be Provided
PART I Basic details of the taxpayer. This will be auto-populated.
PART II Reconciliation of turnover declared in audited Annual Financial Statement with turnover
declared in Annual Return (GSTR9)
PART III Reconciliation of Tax paid.
PART IV Reconciliation of Input Tax Credit.
PART V Additional Liability due to non reconciliation
Module 16: Assessment and Audit: Page 12
01 What is Assessment
Assessment under GST laws has been defined to mean determination of tax liability under GST Acts and it includes self-assessment, re-assessment, provisional assessment, summary assessment and best judgment assessment- Section 2(11) of CGST Act
02 Types of Assessment
03 Process of provisional Assessment
04 General understanding of Audit
• GST is a trust-based taxation regime wherein the assesse is required to self-assess and discharge his tax liability
• Audit in tax law is an important tool for the tax authorities to scrutinize the self-assessed liability determined by the assesse, Compliances undertaken etc to check and ensure compliance of law and prevent any revenue leakage.
• Thus, Audit brings accountability on the part of Taxpayer to properly assess and pay taxes as per the provisions of law and hence makes the tax system more effective
• Under GST Laws, Audit has been defined under Section 2(13) of CGSTAct to mean examination of records, returns and other documents maintained or furnished by the registered person under GST laws, to :
➢ verify the correctness of turnover declared, taxes paid, refund claimed, and input tax credit availed, and
➢ assess his compliance with the provisions of the GSTActs or the rules made thereunder
05 Type of Audit under GST
Audit by Tax Authorities : Audit conducted on order by Commissioner
Special Audit: Audit conducted by a CA/CMAnominated by Commissioner
06 Audit by Tax authorities & 07 Process of Audit by tax authorities
08 Special audit
09 Process of special audit
Entire system is based on trust based assessment and hence the need of audit.
Module 17: Demands and Recovery: Page 18
01 Hierarchy of Officers and monetary limit
02 Time limit for issue of SCN
03 Adjudication order and Time-limits
Demand only against proper notice
04 Summary of Timelines
05 General Provision relating to Determination of Tax
06 Tax collected but not deposited
07 Tax wrongfully collected and paid
08 Recovery Proceedings
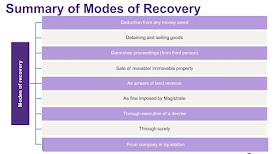
09 Modes of Recovery
10 Garnishee Proceedings
Module 18: Appeals and Advance Ruling: Page 22
01 Understanding of Appeal
General understanding of Appeal
• Dispute arises whenever there is differences in view between the tax-payer and tax officer.
• However, if a taxable person is not satisfied by the decision or order passed by the Adjudicating Authority, then he can appeal to a higher court. The following are the 4 levels of the appeal procedure in GST.
• Now, since India follows a dual GST structure, a natural question which arises is – should an appeal need to be made to both CGST as well as SGST / UTGST authorities?
• As per the provisions of CGST appeals and revisions, both CGST as well as SGST / UTGST officers are empowered to pass orders, and an order passed under CGST will also be deemed to be applied to SGST / UTGST.
• However if an officer under CGST has passed any order, any GST appeal and revisions against that order, will lie only with the officers of CGST. The same will apply in the case or orders passed under SGST / UTGST
02 Hierarchy of Appeal
03 Litigation under GST & Recourse
04 Appeal to appellate authority
05 Revisional authority
06 Appeal to appellate tribunal
07 Appeals to High court
08 Appeals to Supreme Court
09 Authorized representative
10 List of forms for filling appeal
List of forms for filling appeal
Sl. No. Form No. Content
1 GST APL-01 Appeal to AA(Aggrieved person)
2 GST APL-02 Acknowledgement of submission of appeal
3 GST APL-03 Appeal to AA(Authorized officer)
4 GST APL-04 Summary of order indicating final demand
5 GST APL-05 Appeal to the AT(Aggrieved person)
6 GST APL-06 Cross-objections before AT
7 GST APL-07 Appeal to AT(Authorized officer)
8 GST APL-08 Appeal to HC
9 GST RVN-01 Notice by the RA
11 Advance ruling
AAR Miscellaneous provisions
Rectification of Mistakes
• Authority may amend their order to rectify any mistake apparent on the face of the record within a period of six months from the date of the order. (u/s 102 of the CGST Act, 2017)
• However, if such rectification enhances the tax liability or reduces the quantum of input tax credit, the applicant must be heard before the order is passed.
Applicability of Advance Ruling
• An advance ruling pronounced by AAR or AAAR shall be binding only on the applicant and on the concerned officer or the jurisdictional officer in respect of the applicant. (u/s 103 of the CGST Act, 2017)
Time period for applicability
• No specific time period
• Advance ruling shall apply till the period when the law, facts or circumstances supporting original advance ruling have not changed
• Advance ruling shall be held to be ab initio void if obtained by fraud or suppression of material facts or misrepresentation of facts

Module 19 Interest and Penalty Provision: PPT 14
01 Interest on delayed payment of tax
Interest on delayed payment of tax & undue claim of ITC
As per Section 50 of CGST Act, 2017, if GST is not paid within the due dates prescribed for filing of return, then, interest at rates prescribed under GST law must be paid on net tax liability. The same is summarized below:
The interest must be paid by every taxpayer who:
- Delay in payment of GST attracts interest @18% during delay period
- Excess availment and utilization of ITC for payment of GST attracts interest @24% during delay period
02 Interest on undue claim of ITC
03 Late Fee for delayed filling of return
Late Fee for delayed filling of return
As per Section 47 of CGST Act, 2017, late fee is payable when there is delay in filing the GST return. A prescribed late fees will
be charged for each day of delay. The maximum limit of late fee per return for Form GSTR-1 and Form GSTR-3B is
summarized below:
Late Fee for delayed filling of return
Particulars Maximum limit for Late Fees (equally divided into CGST & SGST)
Annual Turnover in last year upto 1.5 cr. 1.5 cr. To 5 cr. Above 5 cr.
Form GSTR-1 2,000 per return 5,000 per return 10,000 per return
Form GSTR-3B 2,000 per return 5,000 per return 10,000 per return
04 Offence and understanding of penalty - 21 offences listed segregated into 3 buckets as below:
05 Personal Penalty
Personal Penalty u/s 122 (3)
Any person who aids or abets any of the offences under Section 122(1) where he acquires possession of, or transports, removes, deposits, keeps, conceals, supplies or purchases or in any other manner deals with any goods which are liable to confiscation under the Act where he receives or is in any way concerned with the supply of services which are in contravention of the Act
Fails to appear before the officer of Central tax, when issued with a summon for appearance to give evidence or produce a document in an inquiry or fails to issue invoice or fails to account for an invoice in his books of accountPenalty to the extent of INR 25,000 (each under CGST and SGST) may be imposed.
06 General Penalty u/s 125
Imposition of penalty upon Any person,
1. who contravenes any provisions the act or rules
2. No penalty is separately provided for in this act
Penalty
1. Maximum INR 25,000 (each in CGST and SGST)
07 General disciplines w.r.t. penalty u/s 126
General disciplines w.r.t. Penalty u/s 126
❖ No officer shall impose penalty for
✓ Minor breaches of tax regulation – tax amount involved is less than INR 5,000
✓ Procedural requirements –
• rectifiable omission or mistake in documentation
• not involving fraud intend
• Error is apparent on the face of record
❖ Penalty to be imposed depending upon facts and circumstances considering degree and severity
❖ Opportunity of being heard
❖ Specify nature of breach and applicable law which imposing penalty in an order
❖ Voluntary disclosure of breach of tax/law etc. prior to discovery – may consider as mitigating factor during
quantification of penalty
❖ The above principle do not apply where penalty is specified in act as fixed sum or fixed %
08 Power to impose and waive off penalty
❖ S. 127 - The officer may issue an order for levying penalty when he is of view that
✓ Person is liable to penalty
✓ The same is not covered under any proceedings u/s 62, 63, 64, 73 or 74 or 129 or 130
✓ After reasonable opportunity of being heard
❖ S. 128 - On recommendation of the Council, the government, by notification:
✓ Waive in part or full,
✓ Penalty u/s 122 (specified offences), 123 (information return) or 125(General penalty) or late fees
✓ For specified taxpayers under mitigating circumstances.
E.g. late fees waived off during covid-19

Module 20 Inspection, Seizure and Arrest PPT7
Provision with higher authority.
01 Inspection
The Joint Commissioner of SGST/CGST (or a higher officer) may have reasons to believe that
a) a taxable person has suppressed any transaction or claimed excess ITC
b) Transporter or own has kept goods which escaped tax;
he can authorize any other officer of CGST/SGST (in FORM GST INS-01) to inspect places of business of the suspected evader.
Inspection of Goods in movement
The Government may intercept and inspect the goods in movement and require the person in charge of a conveyance to produce e-way bill, tax invoice / delivery challan, etc. and devices for verification of the officer.
02 Search and seizure
03 Power to arrest
Power to arrest –Where the Commissioner has reasons to believe that a person has committed any offence specified in
Section 132 (1) (a) or (b) or (c) or (d) which is punishable under clause (i) or (ii) of sub-section (1), or sub-section (2) of the said section, he may, by order, authorize any officer of central tax to arrest such person.
Cognizable offense
• Police can arrest a person without an arrest warrant.
• The arrested person will be informed of the grounds for his arrest.
• Serious crimes like murder, robbery, counterfeiting.
• Appearance before the magistrate within 24 hours
Non-cognizable offence
• Police can not arrest a person without an arrest warrant.
• Shall be admitted to bail or in default of bail, forwarded to the custody of the Magistrate
• The Deputy Commissioner or the Assistant Commissioner shall, for the purpose of releasing an arrested person on bail or otherwise, have the same powers and be subject to the same provisions as an officer-in-charge of a police station.
03Misc. Provisions
The proper office has power to summon persons to give evidence and produce documents.
The proper office shall have access to any place of business of a registered person to inspect books of
account, documents, computers, computer programs etc.
All officers of Police, Railways, Customs, and those officers engaged in the collection of land revenue,
including village officers, officers of State tax and officers of Union territory tax shall assist the proper
officers.
Module 21 Anti-Profiteering PPT7
01 Anti Profiteering - Concept
Anti Profiteering = Anti: opposed to/ against + Profiteering: make or seek to make excessive or unfair profit, often through manipulation of prices or by exploiting a bad or unusual situation
Factors leading to Anti-Profiteering Measure
▪ It has been the experience of many countries that when GST was introduced there has been a marked increase in inflation and the prices of the commodities
▪ In many countries like Australia and Singapore, the inflationary effect has largely been attributed to fact that the benefit accruing due to GST was not passed to the ultimate consumer.
▪ To curb undue profiteering and ensure that the benefit accruing due to implementation of GST is passed on to the consumer, Antiprofiteering provisions have been enacted under GST.
02 Provisions under GST Law
03 Legislative Process
Anti Profiteering: Legislative Process
State level Screening Committee
•To be constituted by respective State Government
•Applications forwarded by interested parties on local issues or application forwarded by Standing Committee is first examined within 2 months from date of receipt
•Relevant cases are forwarded with recommendations to Standing Committee Standing Committee
•Constituted by GST Council by nominating State and Central Government officers.
•Examine the written application within 2 months from the date of receipt from interested party or Commissioner for adequacy and accuracy of the evidence in the application
•If there is prima facie evidence, matter is referred to DG DG of Anti Profiteering
•Before initiating investigation, DG issues notice to interested parties for fair enquiry
•Detailed investigation is conducted by DG, and evidence is collected
•Complete investigation within 6 months from date of receipt from Standing Committee
•Furnish report with its finding to NAA
NAA
•Determination within 6 months from date of receipt of report from DG
•Recommend further investigation or inquiry to DG, if required
•Power to order for reduction of prices, return amount to recipient along with interest, impose penalty or cancel registration




































.JPG)